In this tutorial we are going to learn how find Public IP Address of our computer using Linux curl command.
Normally, if we want to find the public IP Address we use, we go to google and search “what is my ip address”. But if you use Linux, you can get your public IP Address from the command line using curl command.
If your Windows 10 build is 17063, or later, cUrl is included by default. All you need to do is run Command Prompt with administrative rights and you can use cUrl. The Curl.exe is located at C: Windows System32. If you want to be able to use cUrl from anywhere, consider adding it to Path Environment Variables. CUrl On Windows 7, 8/8.1.
The curl command with ifconfig.me argument will show your public IP Address.
For Additional information use curl ifconfig.me/all.
The output will show the public IP Address, user agent and the port you are connected.
So that is how we can easily get the public IP Address using Linux curl command.
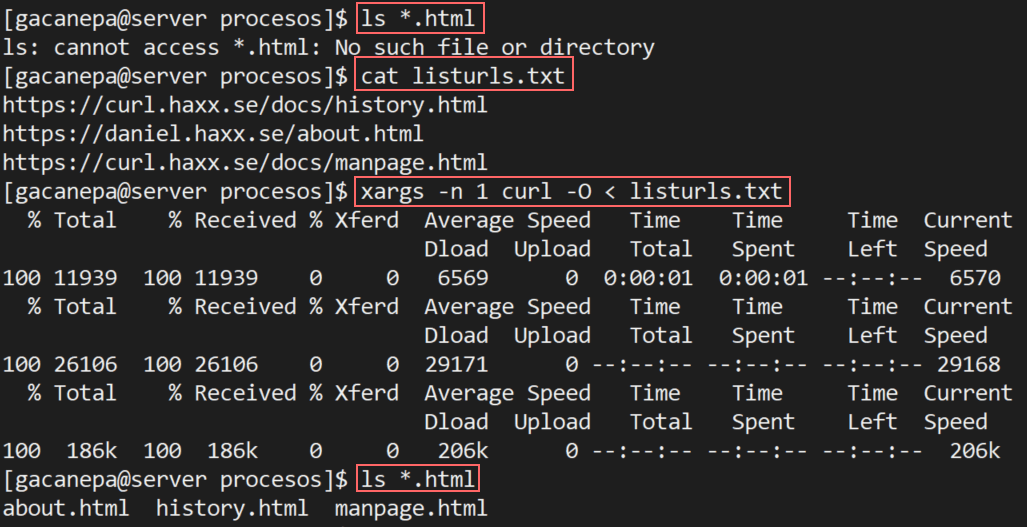
- Curl is a command line tool to transfer data from or to a server Curl is available at the Linux command line, in the Macintosh Terminal and in the Windows Subsystem for Linux. Later versions of Windows 10 include curl in the command prompt. Curl can also be installed from https://curl.haxx.se.
- I don't yet have the reputation necessary to comment on the post that claims curl isn't for ssh or telnet. That is not accurate. Curl handles a multitude of protocols, including telnet, ssh, scp, sftp, ftps, and more. This is the correct syntax for curl: curl -v telnet://127.0.0.1:22.
NAME
curl - transfer a URL
SYNOPSIS
curl [options][URL...]
DESCRIPTION
curl is a tool to transfer data from or to a server, using one of the supported protocols (HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, FTPS, GOPHER, DICT, TELNET, LDAP or FILE). The command is designed to work without user interaction.
curl offers a busload of useful tricks like proxy support, user authentication, ftp upload, HTTP post, SSL (https:) connections, cookies, file transfer resume and more. As you will see below, the amount of features will make your head spin!
curl is powered by libcurl for all transfer-related features. See libcurl (3) for details.
URL
The URL syntax is protocol dependent. You'll find a detailed description in RFC 2396.
You can specify multiple URLs or parts of URLs by writing part sets within braces as in:
http://site.{one,two,three}.com
or you can get sequences of alphanumeric series by using [] as in:
ftp://ftp.numericals.com/file[1-100].txt ftp://ftp.numericals.com/file[001-100].txt (with leading zeros) ftp://ftp.letters.com/file[a-z].txt
No nesting of the sequences is supported at the moment:
http://www.any.org/archive[1996-1999]/volume[1-4]part{a,b,c,index}.html
You can specify any amount of URLs on the command line. They will be fetched in a sequential manner in the specified order.
Curl will attempt to re-use connections for multiple file transfers, so that getting many files from the same server will not do multiple connects / handshakes. This improves speed. Of course this is only done on files specified on a single command line and cannot be used between separate curl invokes.
OPTIONS
-a/--append
(FTP) When used in an FTP upload, this will tell curl to append to the target file instead of overwriting it. If the file doesn't exist, it will be created.
If this option is used twice, the second one will disable append mode again.
-A/--user-agent <agent string>
(HTTP) Specify the User-Agent string to send to the HTTP server. Some badly done CGIs fail if its not set to 'Mozilla/4.0'. To encode blanks in the string, surround the string with single quote marks. This can also be set with the -H/--header option of course.
If this option is set more than once, the last one will be the one that's used.
--anyauth
(HTTP) Tells curl to figure out authentication method by itself, and use the most secure one the remote site claims it supports. This is done by first doing a request and checking the response-headers, thus inducing an extra network round-trip. This is used instead of setting a specific authentication method, which you can do with --basic, --digest, --ntlm, and --negotiate. (Added in 7.10.6)
If this option is used several times, the following occurrences make no difference.
-b/--cookie <name=data>
(HTTP) Pass the data to the HTTP server as a cookie. It is supposedly the data previously received from the server in a 'Set-Cookie:' line. The data should be in the format 'NAME1=VALUE1; NAME2=VALUE2'.
If no '=' letter is used in the line, it is treated as a filename to use to read previously stored cookie lines from, which should be used in this session if they match. Using this method also activates the 'cookie parser' which will make curl record incoming cookies too, which may be handy if you're using this in combination with the -L/--location option. The file format of the file to read cookies from should be plain HTTP headers or the Netscape/Mozilla cookie file format.
NOTE that the file specified with -b/--cookie is only used as input. No cookies will be stored in the file. To store cookies, use the -c/--cookie-jar option or you could even save the HTTP headers to a file using -D/--dump-header!
If this option is set more than once, the last one will be the one that's used.
-B/--use-ascii
Use ASCII transfer when getting an FTP file or LDAP info. For FTP, this can also be enforced by using an URL that ends with ';type=A'. This option causes data sent to stdout to be in text mode for win32 systems.
If this option is used twice, the second one will disable ASCII usage.
--basic
(HTTP) Tells curl to use HTTP Basic authentication. This is the default and this option is usually pointless, unless you use it to override a previously set option that sets a different authentication method (such as --ntlm, --digest and --negotiate). (Added in 7.10.6)
If this option is used several times, the following occurrences make no difference.
--ciphers <list of ciphers>
(SSL) Specifies which ciphers to use in the connection. The list of ciphers must be using valid ciphers. Read up on SSL cipher list details on this URL: http://www.openssl.org/docs/apps/ciphers.html
If this option is used several times, the last one will override the others.
--compressed
(HTTP) Request a compressed response using one of the algorithms libcurl supports, and return the uncompressed document. If this option is used and the server sends an unsupported encoding, Curl will report an error.
If this option is used several times, each occurrence will toggle it on/off.
--connect-timeout <seconds>
Maximum time in seconds that you allow the connection to the server to take. This only limits the connection phase, once curl has connected this option is of no more use. See also the --max-time option.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
-c/--cookie-jar <file name>
Specify to which file you want curl to write all cookies after a completed operation. Curl writes all cookies previously read from a specified file as well as all cookies received from remote server(s). If no cookies are known, no file will be written. The file will be written using the Netscape cookie file format. If you set the file name to a single dash, '-', the cookies will be written to stdout.
NOTE If the cookie jar can't be created or written to, the whole curl operation won't fail or even report an error clearly. Using -v will get a warning displayed, but that is the only visible feedback you get about this possibly lethal situation.
If this option is used several times, the last specfied file name will be used.
-C/--continue-at <offset>
Continue/Resume a previous file transfer at the given offset. The given offset is the exact number of bytes that will be skipped counted from the beginning of the source file before it is transfered to the destination. If used with uploads, the ftp server command SIZE will not be used by curl.
Use '-C -' to tell curl to automatically find out where/how to resume the transfer. It then uses the given output/input files to figure that out.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
--create-dirs
When used in conjunction with the -o option, curl will create the necessary local directory hierarchy as needed.
--crlf
(FTP) Convert LF to CRLF in upload. Useful for MVS (OS/390).
If this option is used twice, the second will again disable crlf converting.
-d/--data <data>
(HTTP) Sends the specified data in a POST request to the HTTP server, in a way that can emulate as if a user has filled in a HTML form and pressed the submit button. Note that the data is sent exactly as specified with no extra processing (with all newlines cut off). The data is expected to be &zerosp;'url-encoded'. This will cause curl to pass the data to the server using the content-type application/x-www-form-urlencoded. Compare to -F/--form. If this option is used more than once on the same command line, the data pieces specified will be merged together with a separating &-letter. Thus, using '-d name=daniel -d skill=lousy' would generate a post chunk that looks like &zerosp;'name=daniel&skill=lousy'.
If you start the data with the letter @, the rest should be a file name to read the data from, or - if you want curl to read the data from stdin. The contents of the file must already be url-encoded. Multiple files can also be specified. Posting data from a file named 'foobar' would thus be done with --data @foobar'.
To post data purely binary, you should instead use the --data-binary option.
-d/--data is the same as --data-ascii.
If this option is used several times, the ones following the first will append data.
--data-ascii <data>
(HTTP) This is an alias for the -d/--data option.
If this option is used several times, the ones following the first will append data.
--data-binary <data>
(HTTP) This posts data in a similar manner as --data-ascii does, although when using this option the entire context of the posted data is kept as-is. If you want to post a binary file without the strip-newlines feature of the --data-ascii option, this is for you.
If this option is used several times, the ones following the first will append data.
--digest
(HTTP) Enables HTTP Digest authentication. This is a authentication that prevents the password from being sent over the wire in clear text. Use this in combination with the normal -u/--user option to set user name and password. See also --ntlm, --negotiate and --anyauth for related options. (Added in curl 7.10.6)
If this option is used several times, the following occurrences make no difference.
--disable-eprt
(FTP) Tell curl to disable the use of the EPRT and LPRT commands when doing active FTP transfers. Curl will normally always first attempt to use EPRT, then LPRT before using PORT, but with this option, it will use PORT right away. EPRT and LPRT are extensions to the original FTP protocol, may not work on all servers but enable more functionality in a better way than the traditional PORT command. (Aded in 7.10.5)
If this option is used several times, each occurrence will toggle this on/off.
--disable-epsv
(FTP) Tell curl to disable the use of the EPSV command when doing passive FTP transfers. Curl will normally always first attempt to use EPSV before PASV, but with this option, it will not try using EPSV.
If this option is used several times, each occurrence will toggle this on/off.
-D/--dump-header <file>
Write the protocol headers to the specified file.
This option is handy to use when you want to store the headers that a HTTP site sends to you. Cookies from the headers could then be read in a second curl invoke by using the -b/--cookie option! The -c/--cookie-jar option is however a better way to store cookies.
When used on FTP, the ftp server response lines are considered being 'headers' and thus are saved there.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
-e/--referer <URL>
(HTTP) Sends the 'Referer Page' information to the HTTP server. This can also be set with the -H/--header flag of course. When used with -L/--location you can append ';auto' to the referer URL to make curl automatically set the previous URL when it follows a Location: header. The ';auto' string can be used alone, even if you don't set an initial referer.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.

--environment
(RISC OS ONLY) Sets a range of environment variables, using the names the -w option supports, to easier allow extraction of useful information after having run curl.
If this option is used several times, each occurrence will toggle this on/off.
--egd-file <file>
(HTTPS) Specify the path name to the Entropy Gathering Daemon socket. The socket is used to seed the random engine for SSL connections. See also the --random-file option.
-E/--cert <certificate[:password]>
(HTTPS) Tells curl to use the specified certificate file when getting a file with HTTPS. The certificate must be in PEM format. If the optional password isn't specified, it will be queried for on the terminal. Note that this certificate is the private key and the private certificate concatenated!
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
--cert-type <type>
(SSL) Tells curl what certificate type the provided certificate is in. PEM, DER and ENG are recognized types.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
--cacert <CA certificate>
(HTTPS) Tells curl to use the specified certificate file to verify the peer. The file may contain multiple CA certificates. The certificate(s) must be in PEM format.
curl recognizes the environment variable named 'CURL_CA_BUNDLE' if that is set, and uses the given path as a path to a CA cert bundle. This option overrides that variable.
The windows version of curl will automatically look for a CA certs file named ´curl-ca-bundle.crt´, either in the same directory as curl.exe, or in the Current Working Directory, or in any folder along your PATH.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
--capath <CA certificate directory>
(HTTPS) Tells curl to use the specified certificate directory to verify the peer. The certificates must be in PEM format, and the directory must have been processed using the c_rehash utility supplied with openssl. Using --capath can allow curl to make https connections much more efficiently than using --cacert if the --cacert file contains many CA certificates.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
-f/--fail
(HTTP) Fail silently (no output at all) on server errors. This is mostly done like this to better enable scripts etc to better deal with failed attempts. In normal cases when a HTTP server fails to deliver a document, it returns a HTML document stating so (which often also describes why and more). This flag will prevent curl from outputting that and fail silently instead.
If this option is used twice, the second will again disable silent failure.
--ftp-create-dirs
(FTP) When an FTP URL/operation uses a path that doesn't currently exist on the server, the standard behavior of curl is to fail. Using this option, curl will instead attempt to create missing directories. (Added in 7.10.7)
If this option is used twice, the second will again disable silent failure.
--ftp-pasv
(FTP) Use PASV when transfering. PASV is the internal default behavior, but using this option can be used to override a previos --ftp-port option. (Added in 7.11.0)
If this option is used twice, the second will again disable silent failure.
--ftp-ssl
(FTP) Make the FTP connection switch to use SSL/TLS. (Added in 7.11.0)
If this option is used twice, the second will again disable silent failure.
-F/--form <name=content>
(HTTP) This lets curl emulate a filled in form in which a user has pressed the submit button. This causes curl to POST data using the content-type multipart/form-data according to RFC1867. This enables uploading of binary files etc. To force the 'content' part to be be a file, prefix the file name with an @ sign. To just get the content part from a file, prefix the file name with the letter <. The difference between @ and < is then that @ makes a file get attached in the post as a file upload, while the < makes a text field and just get the contents for that text field from a file.
Example, to send your password file to the server, where &zerosp;'password' is the name of the form-field to which /etc/passwd will be the input:
curl -F password=@/etc/passwd www.mypasswords.com
To read the file's content from stdin insted of a file, use - where the file name should've been. This goes for both @ and < constructs.
You can also tell curl what Content-Type to use for the file upload part, by using 'type=', in a manner similar to:
curl -F 'web=@index.html;type=text/html' url.com
See further examples and details in the MANUAL.
This option can be used multiple times.
-g/--globoff
This option switches off the 'URL globbing parser'. When you set this option, you can specify URLs that contain the letters {}[] without having them being interpreted by curl itself. Note that these letters are not normal legal URL contents but they should be encoded according to the URI standard.
-G/--get
When used, this option will make all data specified with -d/--data or --data-binary to be used in a HTTP GET request instead of the POST request that otherwise would be used. The data will be appended to the URL with a '?' separator.
If used in combination with -I, the POST data will instead be appended to the URL with a HEAD request.
If used multiple times, nothing special happens.
-h/--help
Usage help.
-H/--header <header>
(HTTP) Extra header to use when getting a web page. You may specify any number of extra headers. Note that if you should add a custom header that has the same name as one of the internal ones curl would use, your externally set header will be used instead of the internal one. This allows you to make even trickier stuff than curl would normally do. You should not replace internally set headers without knowing perfectly well what you're doing. Replacing an internal header with one without content on the right side of the colon will prevent that header from appearing.
See also the -A/--user-agent and -e/--referer options.
This option can be used multiple times to add/replace/remove multiple headers.
-i/--include
(HTTP) Include the HTTP-header in the output. The HTTP-header includes things like server-name, date of the document, HTTP-version and more...
If this option is used twice, the second will again disable header include.
--interface <name>
Perform an operation using a specified interface. You can enter interface name, IP address or host name. An example could look like:
curl --interface eth0:1 http://www.netscape.com/
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
-I/--head
(HTTP/FTP/FILE) Fetch the HTTP-header only! HTTP-servers feature the command HEAD which this uses to get nothing but the header of a document. When used on a FTP or FILE file, curl displays the file size and last modification time only.
If this option is used twice, the second will again disable header only.
-j/--junk-session-cookies
(HTTP) When curl is told to read cookies from a given file, this option will make it discard all 'session cookies'. This will basicly have the same effect as if a new session is started. Typical browsers always discard session cookies when they're closed down. (Added in 7.9.7)
If this option is used several times, each occurrence will toggle this on/off.
-k/--insecure
(SSL) This option explicitly allows curl to perform 'insecure' SSL connections and transfers. Starting with curl 7.10, all SSL connections will be attempted to be made secure by using the CA certificate bundle installed by default. This makes all connections considered 'insecure' to fail unless -k/--insecure is used.
If this option is used twice, the second time will again disable it.
--key <key>
(SSL) Private key file name. Allows you to provide your private key in this separate file.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
--key-type <type>
(SSL) Private key file type. Specify which type your --key provided private key is. DER, PEM and ENG are supported.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
--krb4 <level>
(FTP) Enable kerberos4 authentication and use. The level must be entered and should be one of 'clear', 'safe', 'confidential' or 'private'. Should you use a level that is not one of these, 'private' will instead be used.
This option requiures that the library was built with kerberos4 support. This is not very common. Use -V/--version to see if your curl supports it.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
-K/--config <config file>
Specify which config file to read curl arguments from. The config file is a text file in which command line arguments can be written which then will be used as if they were written on the actual command line. Options and their parameters must be specified on the same config file line. If the parameter is to contain white spaces, the parameter must be inclosed within quotes. If the first column of a config line is a '#' character, the rest of the line will be treated as a comment.
Specify the filename as '-' to make curl read the file from stdin.
Note that to be able to specify a URL in the config file, you need to specify it using the --url option, and not by simply writing the URL on its own line. So, it could look similar to this:
url = 'http://curl.haxx.se/docs/'
This option can be used multiple times.
--limit-rate <speed>
Specify the maximum transfer rate you want curl to use. This feature is useful if you have a limited pipe and you'd like your transfer not use your entire bandwidth.
The given speed is measured in bytes/second, unless a suffix is appended. Appending 'k' or 'K' will count the number as kilobytes, 'm' or M' makes it megabytes while 'g' or 'G' makes it gigabytes. Examples: 200K, 3m and 1G.
If you are also using the -Y/--speed-limit option, that option will take precedence and might cripple the rate-limiting slightly, to help keeping the speed-limit logic working.
This option was introduced in curl 7.10.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
-l/--list-only
(FTP) When listing an FTP directory, this switch forces a name-only view. Especially useful if you want to machine-parse the contents of an FTP directory since the normal directory view doesn't use a standard look or format.
This option causes an FTP NLST command to be sent. Some FTP servers list only files in their response to NLST; they do not include subdirectories and symbolic links.
If this option is used twice, the second will again disable list only.
-L/--location
(HTTP/HTTPS) If the server reports that the requested page has a different location (indicated with the header line Location:) this flag will let curl attempt to reattempt the get on the new place. If used together with -i/--include or -I/--head, headers from all requested pages will be shown. If authentication is used, curl will only send its credentials to the initial host, so if a redirect takes curl to a different host, it won't intercept the user+password. See also --location-trusted on how to change this.
If this option is used twice, the second will again disable location following.
--location-trusted
(HTTP/HTTPS) Like -L/--location, but will allow sending the name + password to all hosts that the site may redirect to. This may or may not introduce a security breach if the site redirects you do a site to which you'll send your authentication info (which is plaintext in the case of HTTP Basic authentication).
If this option is used twice, the second will again disable location following.
--max-filesize <bytes>
Specify the maximum size (in bytes) of a file to download. If the file requested is larger than this value, the transfer will not start and curl will return with exit code 63.
NOTE: The file size is not always known prior to download, and for such files this option has no effect even if the file transfer ends up being larger than this given limit. This concerns both FTP and HTTP transfers.
-m/--max-time <seconds>
Maximum time in seconds that you allow the whole operation to take. This is useful for preventing your batch jobs from hanging for hours due to slow networks or links going down. This doesn't work fully in win32 systems. See also the --connect-timeout option.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
-M/--manual
Manual. Display the huge help text.
-n/--netrc
Makes curl scan the .netrc file in the user's home directory for login name and password. This is typically used for ftp on unix. If used with http, curl will enable user authentication. See netrc(4) or ftp(1) for details on the file format. Curl will not complain if that file hasn't the right permissions (it should not be world nor group readable). The environment variable 'HOME' is used to find the home directory.
A quick and very simple example of how to setup a .netrc to allow curl to ftp to the machine host.domain.com with user name &zerosp;'myself' and password 'secret' should look similar to:
machine host.domain.com login myself password secret
If this option is used twice, the second will again disable netrc usage.
--netrc-optional
Very similar to --netrc, but this option makes the .netrc usage optional and not mandatory as the --netrc does.
--negotiate
(HTTP) Enables GSS-Negotiate authentication. The GSS-Negotiate method was designed by Microsoft and is used in their web aplications. It is primarily meant as a support for Kerberos5 authentication but may be also used along with another authentication methods. For more information see IETF draft draft-brezak-spnego-http-04.txt. (Added in 7.10.6)
This option requiures that the library was built with GSSAPI support. This is not very common. Use -V/--version to see if your version supports GSS-Negotiate.
If this option is used several times, the following occurrences make no difference.
-N/--no-buffer
Disables the buffering of the output stream. In normal work situations, curl will use a standard buffered output stream that will have the effect that it will output the data in chunks, not necessarily exactly when the data arrives. Using this option will disable that buffering.
If this option is used twice, the second will again switch on buffering.
--ntlm
(HTTP) Enables NTLM authentication. The NTLM authentication method was designed by Microsoft and is used by IIS web servers. It is a proprietary protocol, reversed engineered by clever people and implemented in curl based on their efforts. This kind of behavior should not be endorsed, you should encourage everyone who uses NTLM to switch to a public and documented authentication method instead. Such as Digest. (Added in 7.10.6)
If you want to enable NTLM for your proxy authentication, then use --proxy-ntlm.
This option requiures that the library was built with SSL support. Use -V/--version to see if your curl supports NTLM.
If this option is used several times, the following occurrences make no difference.
-o/--output <file>
Write output to <file> instead of stdout. If you are using {} or [] to fetch multiple documents, you can use '#' followed by a number in the <file> specifier. That variable will be replaced with the current string for the URL being fetched. Like in:
curl http://{one,two}.site.com -o 'file_#1.txt'
or use several variables like:
curl http://{site,host}.host[1-5].com -o '#1_#2'
You may use this option as many times as you have number of URLs.
See also the --create-dirs option to create the local directories dynamically.
-O/--remote-name
Write output to a local file named like the remote file we get. (Only the file part of the remote file is used, the path is cut off.)
You may use this option as many times as you have number of URLs.
--pass <phrase>
(SSL) Pass phrase for the private key
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
--proxy-ntlm
Tells curl to use NTLM authentication when communicating with the given proxy. Use --ntlm for enabling NTLM with a remote host.
If this option is used twice, the second will again disable proxy NTLM.
-p/--proxytunnel
When an HTTP proxy is used (-x/--proxy), this option will cause non-HTTP protocols to attempt to tunnel through the proxy instead of merely using it to do HTTP-like operations. The tunnel approach is made with the HTTP proxy CONNECT request and requires that the proxy allows direct connect to the remote port number curl wants to tunnel through to.
If this option is used twice, the second will again disable proxy tunnel.
-P/--ftp-port <address>
(FTP) Reverses the initiator/listener roles when connecting with ftp. This switch makes Curl use the PORT command instead of PASV. In practice, PORT tells the server to connect to the client's specified address and port, while PASV asks the server for an ip address and port to connect to. <address> should be one of:
interface
i.e 'eth0' to specify which interface's IP address you want to use (Unix only)
IP address
i.e '192.168.10.1' to specify exact IP number
host name
i.e 'my.host.domain' to specify machine
-
(any single-letter string) to make it pick the machine's default
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used. Disable the use of PORT with --ftp-pasv. Disable the attempt to use the EPRT command instead of PORT by using --disable-eprt. EPRT is really PORT++.
-q
If used as the first parameter on the command line, the $HOME/.curlrc file will not be read and used as a config file.
-Q/--quote <comand>
(FTP) Send an arbitrary command to the remote FTP server, by using the QUOTE command of the server. Not all servers support this command, and the set of QUOTE commands are server specific! Quote commands are sent BEFORE the transfer is taking place. To make commands take place after a successful transfer, prefix them with a dash '-'. You may specify any amount of commands to be run before and after the transfer. If the server returns failure for one of the commands, the entire operation will be aborted.
This option can be used multiple times.
--random-file <file>
(HTTPS) Specify the path name to file containing what will be considered as random data. The data is used to seed the random engine for SSL connections. See also the --egd-file option.
-r/--range <range>
(HTTP/FTP) Retrieve a byte range (i.e a partial document) from a HTTP/1.1 or FTP server. Ranges can be specified in a number of ways.
0-499 specifies the first 500 bytes
500-999 specifies the second 500 bytes
-500 specifies the last 500 bytes
9500 specifies the bytes from offset 9500 and forward
0-0,-1 specifies the first and last byte only(*)(H)
500-700,600-799 specifies 300 bytes from offset 500(H)
100-199,500-599 specifies two separate 100 bytes ranges(*)(H)
(*) = NOTE that this will cause the server to reply with a multipart response!
You should also be aware that many HTTP/1.1 servers do not have this feature enabled, so that when you attempt to get a range, you'll instead get the whole document.
FTP range downloads only support the simple syntax 'start-stop' (optionally with one of the numbers omitted). It depends on the non-RFC command SIZE.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
-R/--remote-time
When used, this will make libcurl attempt to figure out the timestamp of the remote file, and if that is available make the local file get that same timestamp.
If this option is used twice, the second time disables this again.
-s/--silent
Silent mode. Don't show progress meter or error messages. Makes Curl mute.
If this option is used twice, the second will again disable mute.
-S/--show-error
When used with -s it makes curl show error message if it fails.
If this option is used twice, the second will again disable show error.
--socks <host[:port]>
Use the specified SOCKS5 proxy. If the port number is not specified, it is assumed at port 1080. (Option added in 7.11.1)
This option overrides any previous use of -x/--proxy, as they are mutually exclusive.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
--stderr <file>
Redirect all writes to stderr to the specified file instead. If the file name is a plain '-', it is instead written to stdout. This option has no point when you're using a shell with decent redirecting capabilities.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
-t/--telnet-option <OPT=val>
Pass options to the telnet protocol. Supported options are:
TTYPE=<term> Sets the terminal type.
XDISPLOC=<X display> Sets the X display location.
NEW_ENV=<var,val> Sets an environment variable.
-T/--upload-file <file>
This transfers the specified local file to the remote URL. If there is no file part in the specified URL, Curl will append the local file name. NOTE that you must use a trailing / on the last directory to really prove to Curl that there is no file name or curl will think that your last directory name is the remote file name to use. That will most likely cause the upload operation to fail. If this is used on a http(s) server, the PUT command will be used.
Use the file name '-' (a single dash) to use stdin instead of a given file.
Before 7.10.8, when this option was used several times, the last one was used.
In curl 7.10.8 and later, you can specify one -T for each URL on the command line. Each -T + URL pair specifies what to upload and to where. curl also supports 'globbing' of the -T argument, meaning that you can upload multiple files to a single URL by using the same URL globbing style supported in the URL, like this:
curl -T '{file1,file2}' http://www.uploadtothissite.com
or even
curl -T 'img[1-1000].png' ftp://ftp.picturemania.com/upload/
--trace <file>
Enables a full trace dump of all incoming and outgoing data, including descriptive information, to the given output file. Use '-' as filename to have the output sent to stdout.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used. (Added in 7.9.7)
--trace-ascii <file>
Enables a full trace dump of all incoming and outgoing data, including descriptive information, to the given output file. Use '-' as filename to have the output sent to stdout.
This is very similar to --trace, but leaves out the hex part and only shows the ASCII part of the dump. It makes smaller output that might be easier to read for untrained humans.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used. (Added in 7.9.7)
-u/--user <user:password>
Specify user and password to use for server authentication.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
-U/--proxy-user <user:password>
Specify user and password to use for proxy authentication.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
--url <URL>
Specify a URL to fetch. This option is mostly handy when you want to specify URL(s) in a config file.
This option may be used any number of times. To control where this URL is written, use the -o/--output or the -O/--remote-name options.
-v/--verbose
Makes the fetching more verbose/talkative. Mostly usable for debugging. Lines starting with '>' means data sent by curl, '<' means data received by curl that is hidden in normal cases and lines starting with '*' means additional info provided by curl.
Note that if you want to see HTTP headers in the output, -i/--include might be option you're looking for.
If you think this option still doesn't give you enough details, consider using --trace or --trace-ascii instead.
If this option is used twice, the second will again disable verbose.
-V/--version
Displays information about curl and the libcurl version it uses.
The first line includes the full version of curl, libcurl and other 3rd party libraries linked with the executable.
The second line (starts with 'Protocols:') shows all protocols that libcurl reports to support.
The third line (starts with 'Features:') shows specific features libcurl reports to offer. Available features include:
IPv6
You can use IPv6 with this.
krb4
Krb4 for ftp is supported.
SSL
HTTPS and FTPS are supported.
libz
Automatic decompression of compressed files over HTTP is supported.
NTLM
NTLM authenticaion is supported.
GSS-Negotiate
Negotiate authenticaion is supported.
Debug
This curl uses a libcurl built with Debug. This enables more error-tracking and memory debugging etc. For curl-developers only!
AsynchDNS
This curl uses asynchronous name resolves.
SPNEGO
SPNEGO Negotiate authenticaion is supported.
Largefile
This curl supports transfers of large files, files larger than 2GB.
-w/--write-out <format>
Defines what to display after a completed and successful operation. The format is a string that may contain plain text mixed with any number of variables. The string can be specified as 'string', to get read from a particular file you specify it '@filename' and to tell curl to read the format from stdin you write '@-'.
The variables present in the output format will be substituted by the value or text that curl thinks fit, as described below. All variables are specified like %{variable_name} and to output a normal % you just write them like %%. You can output a newline by using n, a carriage return with r and a tab space with t.
NOTE: The %-letter is a special letter in the win32-environment, where all occurrences of % must be doubled when using this option.
Available variables are at this point:
url_effective The URL that was fetched last. This is mostly meaningful if you've told curl to follow location: headers.
http_code The numerical code that was found in the last retrieved HTTP(S) page.
time_total The total time, in seconds, that the full operation lasted. The time will be displayed with millisecond resolution.
time_namelookup The time, in seconds, it took from the start until the name resolving was completed.
time_connect The time, in seconds, it took from the start until the connect to the remote host (or proxy) was completed.
time_pretransfer The time, in seconds, it took from the start until the file transfer is just about to begin. This includes all pre-transfer commands and negotiations that are specific to the particular protocol(s) involved.
time_starttransfer The time, in seconds, it took from the start until the first byte is just about to be transfered. This includes time_pretransfer and also the time the server needs to calculate the result.
size_download The total amount of bytes that were downloaded.
size_upload The total amount of bytes that were uploaded.
size_header The total amount of bytes of the downloaded headers.
size_request The total amount of bytes that were sent in the HTTP request.
speed_download The average download speed that curl measured for the complete download.
speed_upload The average upload speed that curl measured for the complete upload.
content_type The Content-Type of the requested document, if there was any. (Added in 7.9.5)
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
-x/--proxy <proxyhost[:port]>
Use specified HTTP proxy. If the port number is not specified, it is assumed at port 1080.
This option overrides existing environment variables that sets proxy to use. If there's an environment variable setting a proxy, you can set proxy to &zerosp;' to override it.
Note that all operations that are performed over a HTTP proxy will transparantly be converted to HTTP. It means that certain protocol specific operations might not be available. This is not the case if you can tunnel through the proxy, as done with the -p/--proxytunnel option.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
-X/--request <command>
(HTTP) Specifies a custom request to use when communicating with the HTTP server. The specified request will be used instead of the standard GET. Read the HTTP 1.1 specification for details and explanations.
(FTP) Specifies a custom FTP command to use instead of LIST when doing file lists with ftp.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
-y/--speed-time <time>
If a download is slower than speed-limit bytes per second during a speed-time period, the download gets aborted. If speed-time is used, the default speed-limit will be 1 unless set with -y.
This option controls transfers and thus will not affect slow connects etc. If this is a concern for you, try the --connect-timeout option.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
-Y/--speed-limit <speed>
If a download is slower than this given speed, in bytes per second, for speed-time seconds it gets aborted. speed-time is set with -Y and is 30 if not set.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
-z/--time-cond <date expression>
(HTTP) Request to get a file that has been modified later than the given time and date, or one that has been modified before that time. The date expression can be all sorts of date strings or if it doesn't match any internal ones, it tries to get the time from a given file name instead! See the GNU date(1) or curl_getdate(3) man pages for date expression details.
Start the date expression with a dash (-) to make it request for a document that is older than the given date/time, default is a document that is newer than the specified date/time.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
-Z/--max-redirs <num>
Set maximum number of redirection-followings allowed. If -L/--location is used, this option can be used to prevent curl from following redirections &zerosp;'in absurdum'.
If this option is used several times, the last one will be used.
-0/--http1.0
(HTTP) Forces curl to issue its requests using HTTP 1.0 instead of using its internally preferred: HTTP 1.1.
-1/--tlsv1
(HTTPS) Forces curl to use TSL version 1 when negotiating with a remote TLS server.
-2/--sslv2
(HTTPS) Forces curl to use SSL version 2 when negotiating with a remote SSL server.
-3/--sslv3
(HTTPS) Forces curl to use SSL version 3 when negotiating with a remote SSL server.
-4/--ipv4
If libcurl is capable of resolving an address to multiple IP versions (which it is if it is ipv6-capable), this option tells libcurl to resolve names to IPv4 addresses only. (Added in 7.10.8)
-6/--ipv6
If libcurl is capable of resolving an address to multiple IP versions (which it is if it is ipv6-capable), this option tells libcurl to resolve names to IPv6 addresses only. (Added in 7.10.8)
-#/--progress-bar
Make curl display progress information as a progress bar instead of the default statistics.
If this option is used twice, the second will again disable the progress bar.
FILES
~/.curlrc
Default config file.
ENVIRONMENT
http_proxy [protocol://]<host>[:port]
Sets proxy server to use for HTTP.
HTTPS_PROXY [protocol://]<host>[:port]
Sets proxy server to use for HTTPS.
FTP_PROXY [protocol://]<host>[:port]
Sets proxy server to use for FTP.
GOPHER_PROXY [protocol://]<host>[:port]
Sets proxy server to use for GOPHER.
ALL_PROXY [protocol://]<host>[:port]
Sets proxy server to use if no protocol-specific proxy is set.
NO_PROXY <comma-separated list of hosts>
list of host names that shouldn't go through any proxy. If set to a asterisk '*' only, it matches all hosts.
EXIT CODES
There exists a bunch of different error codes and their corresponding error messages that may appear during bad conditions. At the time of this writing, the exit codes are:
1
Unsupported protocol. This build of curl has no support for this protocol.
2
Failed to initialize.
3
URL malformat. The syntax was not correct.
4
URL user malformatted. The user-part of the URL syntax was not correct.
5
Couldn't resolve proxy. The given proxy host could not be resolved.
6
Couldn't resolve host. The given remote host was not resolved.
7
Failed to connect to host.
8
FTP weird server reply. The server sent data curl couldn't parse.
9
FTP access denied. The server denied login.
10
FTP user/password incorrect. Either one or both were not accepted by the server.
11
FTP weird PASS reply. Curl couldn't parse the reply sent to the PASS request.
12
FTP weird USER reply. Curl couldn't parse the reply sent to the USER request.
13
FTP weird PASV reply, Curl couldn't parse the reply sent to the PASV request.
14
FTP weird 227 format. Curl couldn't parse the 227-line the server sent.
15
FTP can't get host. Couldn't resolve the host IP we got in the 227-line.
16
FTP can't reconnect. Couldn't connect to the host we got in the 227-line.
17
FTP couldn't set binary. Couldn't change transfer method to binary.
18
Partial file. Only a part of the file was transfered.
19
FTP couldn't download/access the given file, the RETR (or similar) command failed.
20
FTP write error. The transfer was reported bad by the server.
21
FTP quote error. A quote command returned error from the server.
22
HTTP page not retrieved. The requested url was not found or returned another error with the HTTP error code being 400 or above. This return code only appears if -f/--fail is used.
23
Write error. Curl couldn't write data to a local filesystem or similar.
24
Malformed user. User name badly specified.
25
FTP couldn't STOR file. The server denied the STOR operation, used for FTP uploading.
26
Read error. Various reading problems.
27
Out of memory. A memory allocation request failed.
28
Operation timeout. The specified time-out period was reached according to the conditions.
29
FTP couldn't set ASCII. The server returned an unknown reply.
30
FTP PORT failed. The PORT command failed. Not all FTP servers support the PORT command, try doing a transfer using PASV instead!
31
FTP couldn't use REST. The REST command failed. This command is used for resumed FTP transfers.
32
FTP couldn't use SIZE. The SIZE command failed. The command is an extension to the original FTP spec RFC 959.
Curl Port 80
33
HTTP range error. The range 'command' didn't work.
34
HTTP post error. Internal post-request generation error.
35
SSL connect error. The SSL handshaking failed.
36
FTP bad download resume. Couldn't continue an earlier aborted download.
37
FILE couldn't read file. Failed to open the file. Permissions?
38
LDAP cannot bind. LDAP bind operation failed.
39
LDAP search failed.
40
Library not found. The LDAP library was not found.
41
Function not found. A required LDAP function was not found.
42
Aborted by callback. An application told curl to abort the operation.
43
Internal error. A function was called with a bad parameter.
44
Internal error. A function was called in a bad order.
45
Interface error. A specified outgoing interface could not be used.
46
Bad password entered. An error was signaled when the password was entered.
47
Too many redirects. When following redirects, curl hit the maximum amount.
48
Unknown TELNET option specified.
49
Malformed telnet option.
51
The remote peer's SSL certificate wasn't ok
52
The server didn't reply anything, which here is considered an error.
53
SSL crypto engine not found
54
Cannot set SSL crypto engine as default
55
Failed sending network data
56
Failure in receiving network data
57
Share is in use (internal error)
58
Problem with the local certificate
59
Couldn't use specified SSL cipher
60
Problem with the CA cert (path? permission?)
61
Unrecognized transfer encoding
62
Invalid LDAP URL
63
Maximum file size exceeded
XX
There will appear more error codes here in future releases. The existing ones are meant to never change.
AUTHORS / CONTRIBUTORS
Curl Port Number Ended With
Daniel Stenberg is the main author, but the whole list of contributors is found in the separate THANKS file.
WWW
FTP
Curl Port 443 Connection Refused
ftp://ftp.sunet.se/pub/www/utilities/curl/
SEE ALSO
ftp (1)wget (1)snarf (1)
Using Curl To Check Port
This HTML page was made with roffit.
